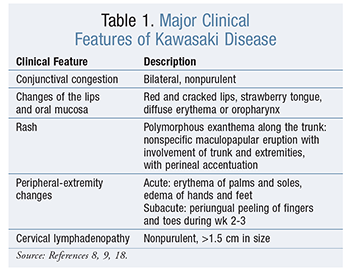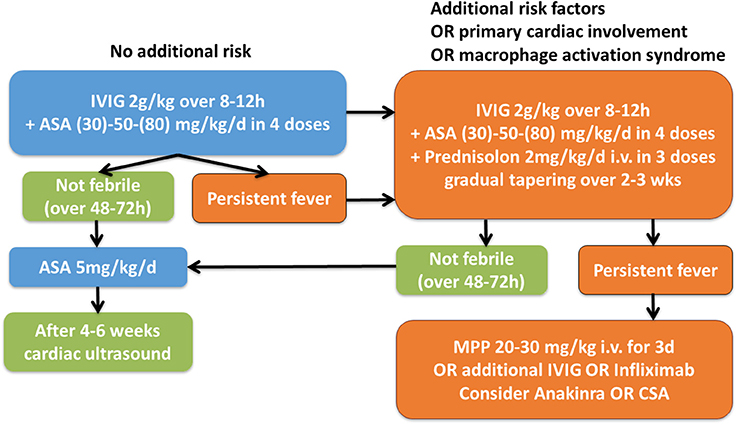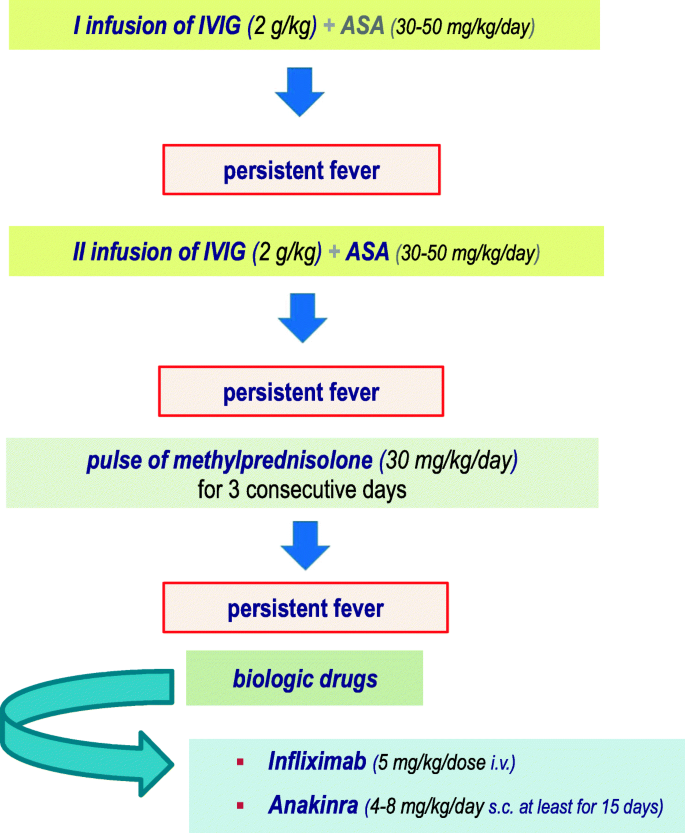
Revised recommendations of the Italian Society of Pediatrics about the general management of Kawasaki disease | Italian Journal of Pediatrics | Full Text
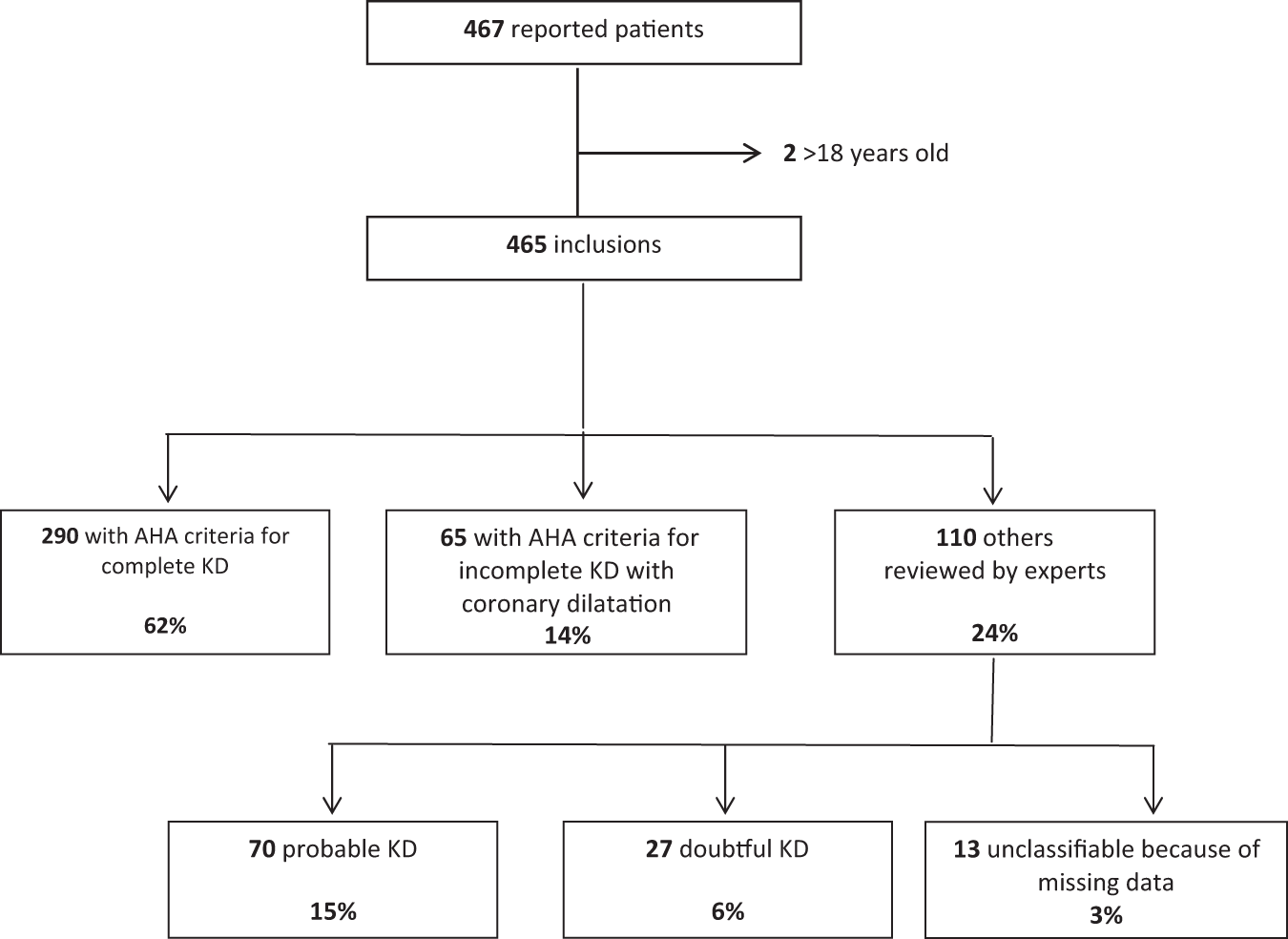
Defining the risk of first intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in non-Asian patients with Kawasaki disease | Scientific Reports
Unique Molecular Patterns Uncovered in Kawasaki Disease Patients with Elevated Serum Gamma Glutamyl Transferase Levels: Implications for Intravenous Immunoglobulin Responsiveness | PLOS ONE

Kawasaki Dis Canada su Twitter: "Approximately 10% to 20% of patients with Kawasaki disease develop recrudescent or persistent fever at least 36 hours after the end of their IVIG infusion and are

Kawasaki disease: Aetiopathogenesis and therapeutic utility of intravenous immunoglobulin | Semantic Scholar

Efficacy of immunoglobulin plus prednisolone for prevention of coronary artery abnormalities in severe Kawasaki disease (RAISE study): a randomised, open-label, blinded-endpoints trial - The Lancet
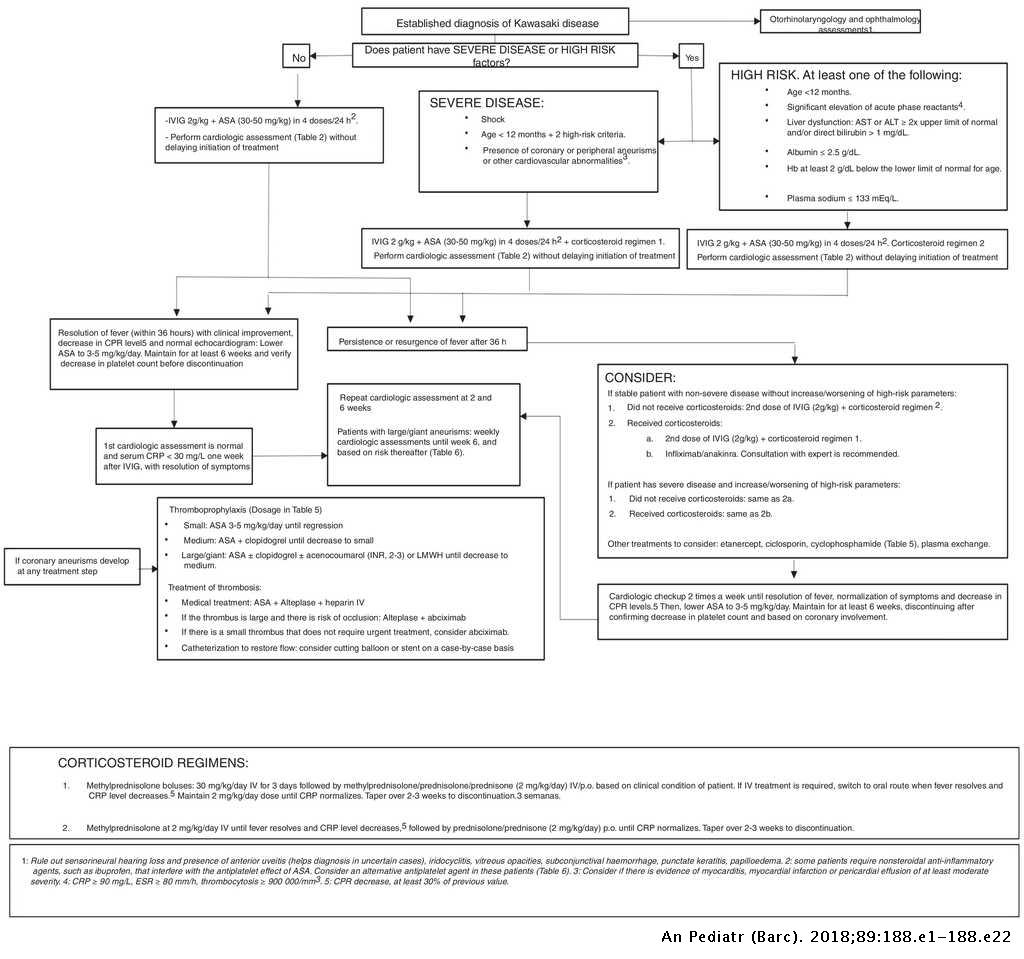
National consensus on the cardiological treatment and follow-up of Kawasaki disease | Anales de Pediatría
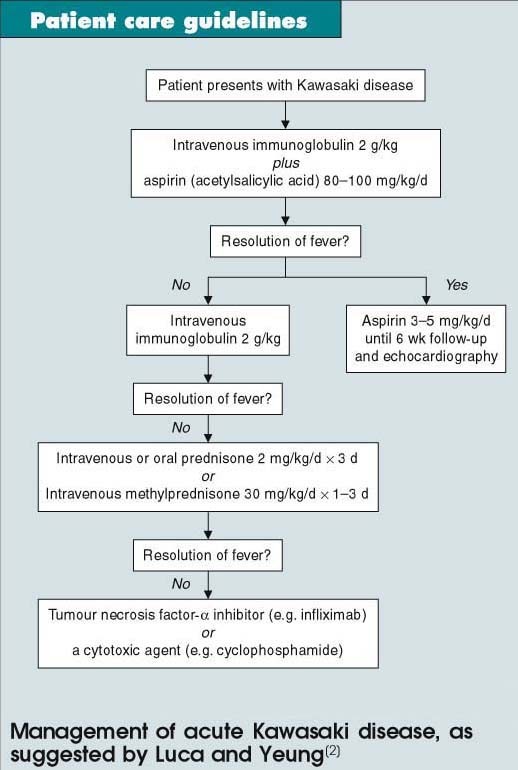
Treat acute Kawasaki disease with aspirin plus intravenous immunoglobulin to improve coronary outcomes | SpringerLink

Efficacy of primary treatment with immunoglobulin plus ciclosporin for prevention of coronary artery abnormalities in patients with Kawasaki disease predicted to be at increased risk of non-response to intravenous immunoglobulin (KAICA): a